Adaptive Payments API: Getting Started
Full source code is available here
This guide presents the following sections to quickly get you up and running with
the Adaptive Payments API:
Overview
The Adaptive Payments API enables merchants and developers to select the payment
scenario most suitable to their needs. Merchants and developers can create applications
that manage payments, payment preapprovals, and refunds. Merchants and developers
can also send money peer-to-peer, split payments in both
parallel and
chained models,
accept
guest payments,
, and schedule disbursements. It works on multiple platforms including the web and
mobile environments.
Key Concepts
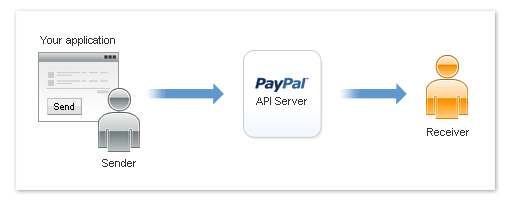
Adaptive Payments has operations that enable the sending and receiving of payments
involving two or more parties. Each Adaptive Payments API transaction includes a
sender and one or more receivers of the payment. Each transaction also includes
the application owner, called the "API Caller," who is an invisible third
party that provides the transaction flow and is the entity that makes the API calls.
In most scenarios, payment transactions are initiated by the buyer (in asend type
of payment arrangement) or by the seller (in a pay type of payment
arrangement).
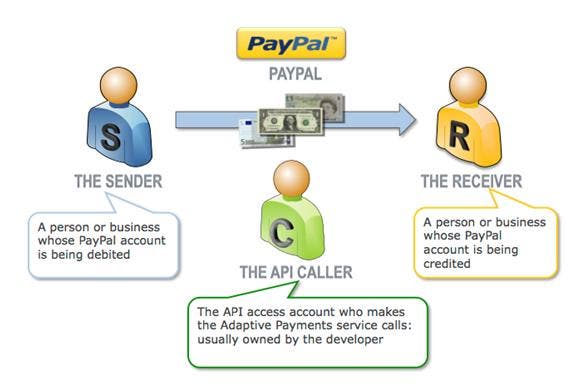 Figure 1.
Figure 1. Overview of Adaptive Payments
The Adaptive Payments API uses the Pay operation
to make payments between a sender and one or more receivers of that payment. Payments
can be split between receivers (in either "chained" or "parallel"
modes) and additional operations in the API lets senders authorize and preapprove
an application to make payments on their behalf. The flexibility of the operations
in the API make for an "adaptive" set of functions that addresses a wide
range of payment scenarios.
Payment Approvals
As with any payment, the payments made via the Adaptive Payments API must be authorized
and approved by the payment sender. To provide the best possible user experience
for senders, the Adaptive Payments API provides the following payment approval methods:
- Web Redirect
- The default
method where applications redirect the sender of the payment to PayPal for approval.
- Embedded Process
- Applications
embed the payment authorization process into the application itself.
- Implicit
- Applications act as the sender of the payment and implicitly authorize
the payment.
- Preapproved
- Applications
obtain a preapproval from the sender.
Making Your First Call
To make a call to the Adaptive Payments Pay operation,
supply the necessary HTTP headers and call payload to the service
endpoint.
A call to the Pay operation
involves three users:
- API Caller, represents your application and the account whose credentials the application
uses to make the call
- Sender, the account making the payment
- Receiver, the account receiving the payment
The following steps outline the inputs needed to make the call and shows how to
authorize the payment after the Pay operation
succeeds:
- Obtain the endpoint for the service and environment you are addressing.
The Sandbox endpoint for the Adaptive Payments Pay operation
is:
https://svcs.sandbox.paypal.com/AdaptivePayments/Pay
- Format the HTTP headers needed to make the call.
You need to supply the following headers to call the Pay operation:
X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-USERID : Sandbox-Caller-User-Id
X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-PASSWORD : Sandbox-Caller-Password
X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-SIGNATURE : Sandbox-Caller-Security-Signature
X-PAYPAL-APPLICATION-ID : APP-80W284485P519543T
X-PAYPAL-REQUEST-DATA-FORMAT : JSON
X-PAYPAL-RESPONSE-DATA-FORMAT : JSON
- Format the call payload.
The Pay operation
requires several payload input fields, shown here as a JSON object:
{
"actionType":"PAY",
"currencyCode":"USD",
"receiverList":{"receiver":[{
"amount":"1.00",
"email":"Sandbox-Receiver-eMail"}]
},
"returnUrl":"http://Payment-Success-URL",
"cancelUrl":"http://Payment-Cancel-URL",
"requestEnvelope":{
"errorLanguage":"en_US",
"detailLevel":"ReturnAll"
}
}
That's it, you're now set to make the call.
- Make the call.
- If your
Pay call
is successful (the ack field
in the response contains Success),
redirect the Sender to PayPal so they can authorize the payment:
- Retrieve the
payKey value
from the response of the Pay call.
Here is an example of a successful Pay response
with the payKey highlighted:
{
"responseEnvelope": {
"timestamp": "2011-08-20T15:12:20.833-07:00",
"ack": "Success",
"correlationId": "nnnnnnnnnnnn",
"build": "nnnnnnn"
},
"payKey": "Your-payKey",
"paymentExecStatus": "CREATED"
}
- Use the
payKey value
in an authorization redirect to PayPal using the following Sandbox URI:
https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_ap-payment&paykey=
Your-payKey
When redirected to PayPal, the Sender is presented with a PayPal Authorization window
where they can login to their account and approve the payment.
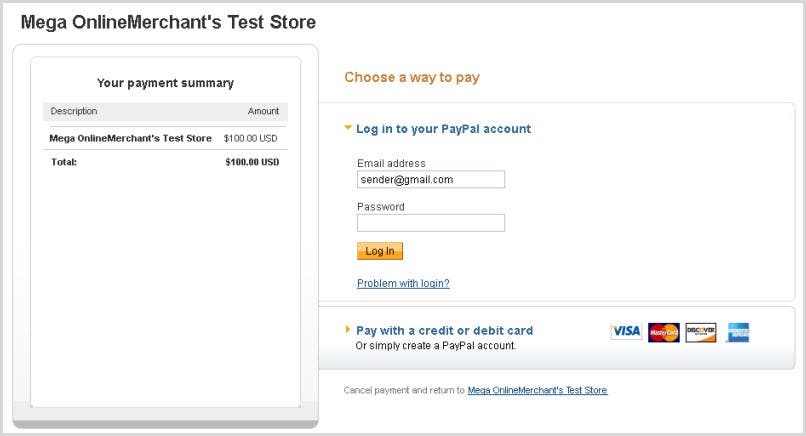 Figure 2.
Figure 2. Authorizing the Payment
Once the buyer authorizes the payment, the transaction is complete and they are
redirected to the URL specified by the returnUrl input
field in your Payrequest.
Try It!
The following cURL command contains a call to the
Pay operation.
Run the command by copying and pasting it into a code window. (If cURL is not installed
on your system, you can download the free cURL executable from
http://curl.haxx.se/download.html.)
curl -s --insecure -H "X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-USERID: caller_1312486258_biz_api1.gmail.com" -H "X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-PASSWORD: 1312486294" -H "X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-SIGNATURE: AbtI7HV1xB428VygBUcIhARzxch4AL65.T18CTeylixNNxDZUu0iO87e" -H "X-PAYPAL-REQUEST-DATA-FORMAT: JSON" -H "X-PAYPAL-RESPONSE-DATA-FORMAT: JSON" -H "X-PAYPAL-APPLICATION-ID: APP-80W284485P519543T" https://svcs.sandbox.paypal.com/AdaptivePayments/Pay -d "{\"actionType\":\"PAY\", \"currencyCode\":\"USD\", \"receiverList\":{\"receiver\":[{\"amount\":\"1.00\",\"email\":\"rec1_1312486368_biz@gmail.com\"}]}, \"returnUrl\":\"http://www.example.com/success.html\", \"cancelUrl\":\"http://www.example.com/failure.html\", \"requestEnvelope\":{\"errorLanguage\":\"en_US\", \"detailLevel\":\"ReturnAll\"}}"
Voilà! You have made your first call to the Adaptive
Payments API.
After issuing the command, the Adaptive Payments service should return a successful
response that includes a valid Sandbox payKey.
The above call is made possible by the use of a publicly-available set of Sandbox
credentials (highlighted in the call). While you can extract the payKey from
the response and use it in an authorization redirect, you will be unable to authorize
the Sandbox transaction. However, if you substitute the credentials and e-mail address
from your Sandbox test accounts into the above command, you will be able to complete
the entire transaction flow in the Sandbox.
If, after using your own Sandbox credentials, your Pay call
is not successful, review the call response for the error details and address the
problem before resubmitting the call. If your call is successful, insert the returned payKey value
into the following URL:
https://www.sandbox.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_ap-payment&paykey=payKey
Log in to the resulting PayPal window with your Sandbox Buyer account to complete
the transaction. Once complete, log into your Sandbox account and review the test
account balances and e-mail to see the transaction results.
Introducing Adaptive Payments
The Adaptive Payments API enables you to send money in many different scenarios,
from simple to complex. For example, you might build a small send money application
for a social networking site or a robust payroll system.
Adaptive Payments Actors and Objects
Adaptive payments handles payments between a sender of a payment
and one or more receivers of the payment. You are an application
owner, such as a merchant that owns a website, the owner of a widget on
a social networking site, the provider of a payment application on mobile phones,
and so on. Your application is the caller of Adaptive Payments API operations.
Note: The application owner must have a PayPal Business account.
Senders and receivers can have any PayPal account type. Senders and receivers are
not required to have PayPal accounts initially. PayPal prompts a sender to create
an account before a payment can be completed. A receiver must create an account
to receive the funds after the payment completes.
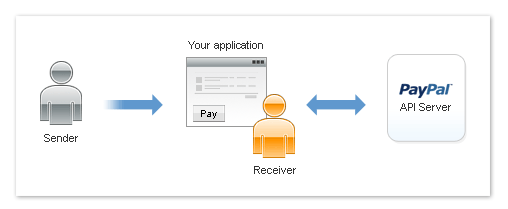
With many applications, you may be both the application owner and a receiver. For
example, as the owner of a website, you are the receiver of payments from the senders
who are your customers. The following diagram shows the relationship between a sender,
you as a receiver, and PayPal:
You are not required to be a receiver. For example, if you own a shopping cart,
you are not required to receive payments directly. You can facilitate payments between
the sender and receivers that provide the actual goods. The following diagram shows
the relationship between a sender, you as an application owner that directs payments
to receivers, and PayPal:

This diagram shows a payment in which the sender pays multiple receivers in a parallel
payment. With parallel payments, the sender can see the transaction to each receiver.
The following diagram shows the relationship between a sender, you as an application
owner that directs payments to receivers, and PayPal in a chained payment:
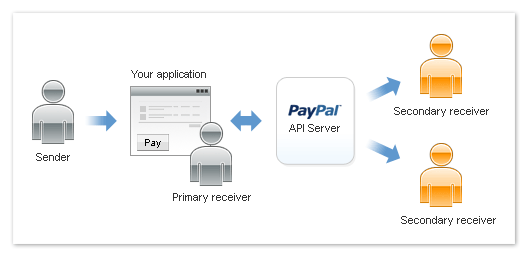
In a chained payment, the sender pays the primary receiver an amount, from which
the primary receiver pays secondary receivers. The sender only knows about the primary
receiver, not the secondary receivers. The secondary receivers only know about the
primary receiver, not the sender.
The following diagram shows the relationship between you as both the sender and
the application owner that directs payments to receivers:
For example, you might use this configuration in a sales commission application
that transfers funds owed for commissions from your account to the accounts of your
sales force.
Simple, Parallel, and Chained Payments
Adaptive Payments provides several kinds of payment: simple, parallel, and chained
payments. You create each kind of payment with the Pay API.
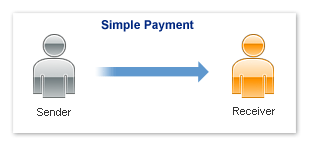
Simple Payments
Simple payments enable a sender to send a single payment to a single receiver. This
is sometimes considered a traditional payment, such as a payment from a buyer to
a seller.
Scenarios involving simple payments might include the following scenarios:
- Buyer makes a payment on a merchant's website.
- Buyer makes a single payment for a cart of items from the same merchant.
- Person on a social networking site makes a payment for a purchase to the receiver.
For example, a sender sends money to pay for lunch at a restaurant.
In these cases, the sender sends a payment to a single receiver. The following example
shows a sender making a simple payment:
Parallel Payments
A parallel payment is a payment from a sender that is split directly among 2-6 receivers.
Technically, a parallel payment is a set of multiple payments made in a single Pay request.
Parallel payments are useful in cases when a buyer intends to make a single payment
for items from multiple sellers. Examples include the following scenarios:
- a single payment for multiple items from different merchants, such as a combination
of items in your inventory and items that partners drop ship for you.
- purchases of items related to an event, such as a trip that requires airfare, car
rental, and a hotel booking.
In these cases, the sender knows the receivers and the amount paid to each one.
The following example shows a sender paying 3 receivers in a single parallel payment:
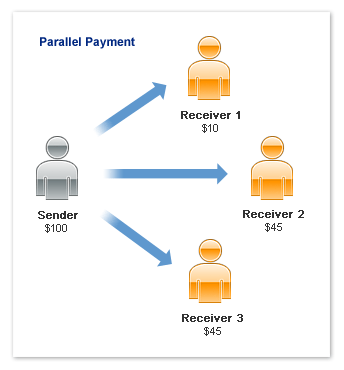
Note: This scenario is an example only and does not take PayPal
fees into account.
Chained Payments
A chained payment is a payment from a sender that is indirectly split among multiple
receivers. It is an extension of a typical payment from a sender to a receiver,
in which a receiver, known as the primary receiver, passes part of
the payment to other receivers, who are called secondary receivers.
Note: The API caller must get permission from PayPal to use
chained payments.
You can have at most one primary receiver and 1-5 secondary receivers. Chained payments
are useful in cases when the primary receiver acts as an agent for other receivers.
The sender deals only with the primary receiver and does not know about the secondary
receivers, including how a payment is split among receivers. The following example
shows a sender making a payment of $100:
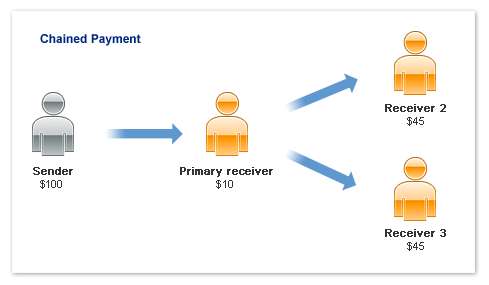
In this example, the primary receiver receives $100 from the sender's perspective.
The primary receiver actually receives only $10 and passes a total of $90 to secondary
receivers, Receiver 2 and Receiver 3.
Note: This scenario is an example only and does not take PayPal
fees into account.
Delayed Chained Payments
By default, payments to all receivers in a chained payment are immediate. However,
you can choose to delay a payment to a secondary receiver. For example, as primary
receiver, you may require secondary receivers to perform some action, such as shipping
goods or waiting for expiration of a return period, before making payment. To complete
the payment, you must explicitly execute a payment to secondary receivers after
the sender pays you. The payment must occur within 90 days, after which you cannot
complete the payment as part of the original chained payment.
Payment Approval
The sender of a payment must approve the transfer. The sender can log in to paypal.com
to approve each payment, preapprove payments, or when the sender is your application,
be implicitly approved to make payments.
Note: Preapproval requests require permission from PayPal.
There are 3 kinds of payment approvals:
- Explicit approval payments, in which the sender logs in to paypal.com to approve
each payment. Explicitly approving payments is the traditional way to pay with PayPal.
This method is the only option unless the sender has set up a preapproval agreement
or you, the API caller, are also the sender.
- Preapproved payments, in which a sender logs in to PayPal and sets up preapprovals
that approve future payments or set up a preapproval during the embedded payment
flow. The sender logs in to paypal.com once to set up the preapproval. After the
sender agrees to the preapproval, specific approval is unnecessary.
- Implicit approval payments, in which your application is both the sender of a payment
and the caller of the Adaptive Payments
Pay API.
In this case, PayPal makes the payment from your own account, which eliminates the
need for approval.
Adaptive Payments Service Permissions
Adaptive Payments services are divided into 2 categories: standard services that
do not require specific permission to use and advanced services that
require permission from PayPal to use. You obtain permission to use a service when
you submit an application to PayPal.
You can use the following standard services without requesting specific permission:
- Making simple or parallel payments that require explicit approval of the sender
- Getting payment details
- Making refunds
- Performing currency conversions
To use any other service, you must receive permission from PayPal to use the service
when you submit your application. For example, if your application makes chained
payments, which is an advanced service, you request permission when you submit your
application. Later, if you modify your application to support preapprovals, which
is also an advanced service, you must resubmit your application to obtain permission
from PayPal to use the service.
 Important:
Important: If
you allow a third party to PayPal to execute an application on your behalf, the
third party becomes the API caller because the party is now calling the Adaptive
Payments API. The third party must also have permission from PayPal to use the advanced
service. For example, if an application supports chained payments, both you and
the third party must have permission to use the service.
Explicit Approval Payment Flow
Explicit approval payments require the sender to log in to paypal.com to approve
the payment. You control the interaction between your application and PayPal by
specifying URLs for redirection in various situations.
The following diagram shows the basic flow of control for a payment (such as payment
for items in a shopping cart at a web store) that requires the sender to log in
to paypal.com to approve the payment:
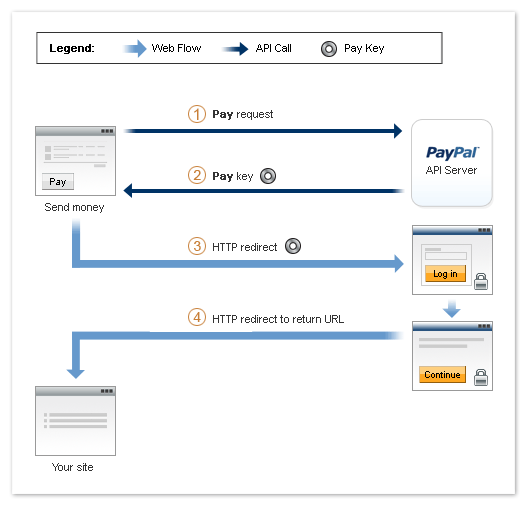
The following items correspond to the circled numbers in the diagram:
- Your site or device sends a
Pay request
to PayPal on behalf of a sender.
- PayPal responds with a key that you use when you direct the sender to PayPal.
- You redirect your sender's browser to paypal.com.
- After the sender authorizes the transfer of funds, PayPal redirects your sender's
browser to the location you specify.
Note: The cancel operation is not shown in the diagram. Cancellation
is handled by a separate cancellation URL to which PayPal redirects the sender's
browser any time the sender cancels while on paypal.com.
In addition to these steps, PayPal notifies you and the sender of the payment.
Preapproved Payments Flow
Preapproved payments require the sender to log in to paypal.com to set up the payment
agreement with a particular vendor. You control the interaction between your application
and PayPal by specifying URLs for redirection in various situations.
The sender logs in to paypal.com and sets up the preapproval, which includes setting
the following information:
- duration of the preapproval, from the start date to the end date, inclusive
- the maximum amount being preapproved
- the maximum number of payments
The following diagram shows the basic flow of control during a preapproval operation:
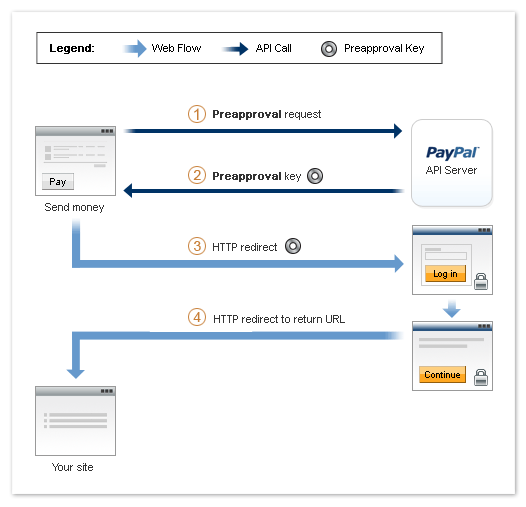
The following items correspond to the circled numbers in the diagram:
- Your site or device sends a
Preapproval request
to PayPal on behalf of a sender.
- PayPal responds with a key, called a preapproval key, that you use
when you direct the sender to PayPal, and once the preapproval has been established,
whenever you automatically complete a payment on behalf of the sender.
- You redirect your sender's browser to PayPal.
- After the sender logs in to paypal.com and sets up the preapproval, PayPal redirects
the sender's browser to a location you specify.
Note: The cancel operation is not shown in the above diagram.
Cancellation is handled by a separate cancellation URL to which PayPal redirects
the sender's browser any time the sender cancels while on paypal.com.
In addition to the steps shown above, PayPal sends an email notifying you and the
sender that the preapproval has been created.
After the sender sets up the approval, you can make payments on the sender's behalf
directly. The sender is no longer required to log in to PayPal to complete the payment.
The following diagram shows the basic flow of control during a Pay operation:
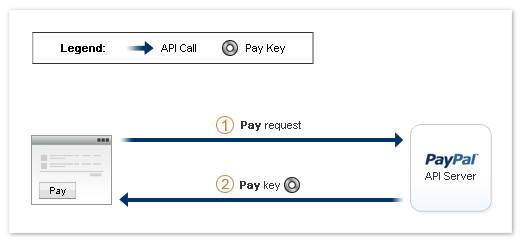
The following items correspond to the circled numbers in the diagram:
- Your site or device sends a
Pay request
to PayPal on behalf of a sender. You can require the sender to provide a personal
identification number (PIN); however, logging in to paypal.com is no longer required.
Note: You must provide a preapproval key that identifies the
agreement.
- PayPal still responds with a payment key that you can use for other API operations,
such as for obtaining details of the payment or for issuing a refund.
Implicit Approval Payments Flow
Implicit approval payments are payments where the sender and the API caller are
using the same account. Because PayPal draws the funds for the payment from your
own account, there is no approval necessary, and as such there is no visible flow
for implicit approval payments.
The following diagram shows the basic flow of control during an implicitly approved
payment operation:

The following items correspond to the circled numbers in the diagram:
- Your site or device sends a
Pay request
to PayPal.
Note: A web flow is not required.
- PayPal responds with a key that you use for other API operations.
Embedded Payments
An embedded payment is a payment that initiates a visual presentation
of the Adaptive Payments payment flow in which the sender appears to never leave
your checkout or payment page. Embedded payments make it easier for a sender to
make a payment because PayPal may allow the sender to bypass the PayPal login step.
The ability to bypass the login relies on a remember
me cookie, which is stored in the sender's browser when the sender
chooses to take advantage of being remembered. Opting in reduces the number of steps
to purchase goods or services without significantly increasing the risk that the
sender's account might be misused. After the initial login, PayPal bypasses the
login step if subsequent payments meet specific criteria, such as a subsequent payment
for a small amount.
Embedded Payment Flow Presentations
PayPal provides the following kinds of visual presentations for the embedded payment
flow:
- The payment flow can be embedded as a lightbox on your web page, which gives the
impression that the payment is handled completely within your website:
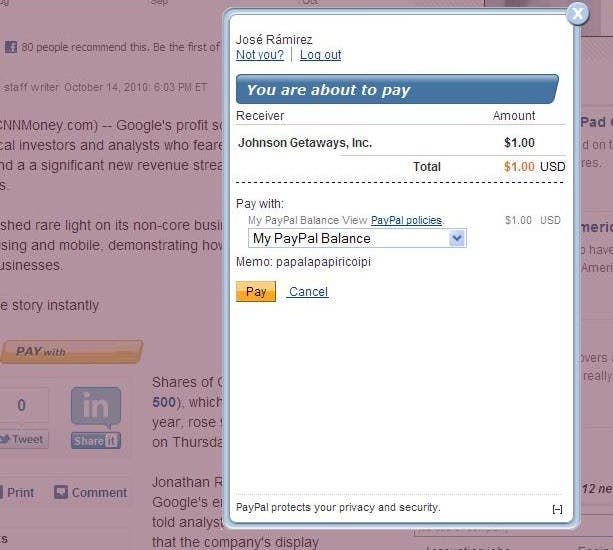
- The payment flow can appear in a minibrowser window that appears in front of your
web page, which does not require an IFRAME:
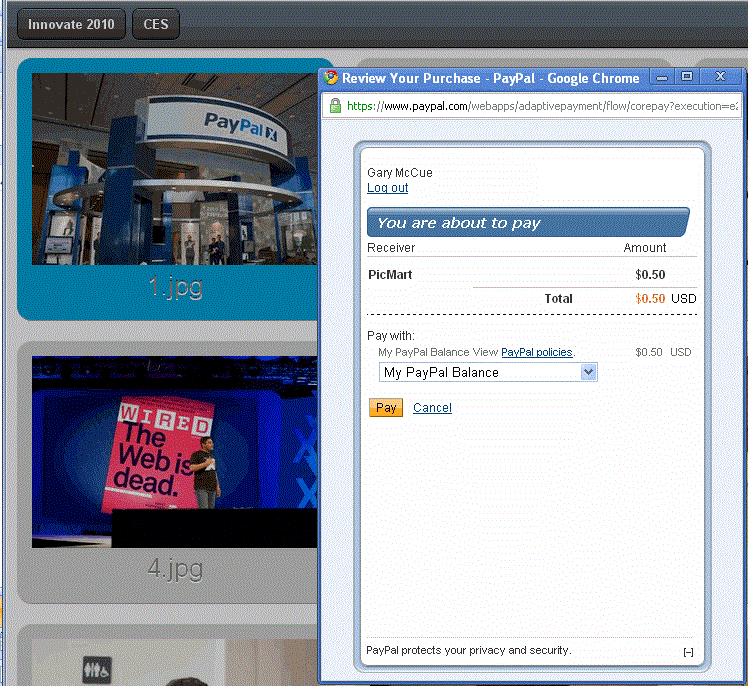
- The payment flow can be embedded as a lightbox in an IFRAME on your web page, which
gives the impression that the payment is handled completely within your website:
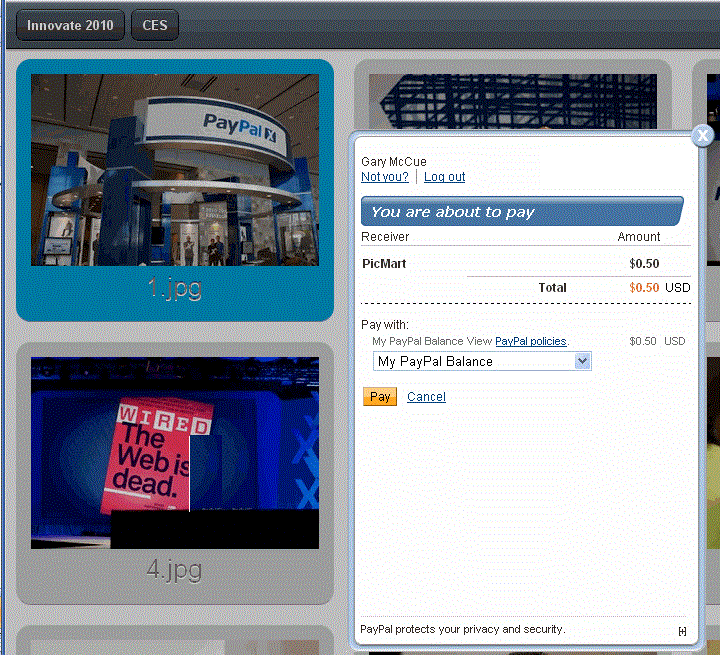
You choose your preferred visual presentation when you invoke the embedded payment
flow. In some cases, PayPal may override your choice to use a lightbox; for example,
when the sender is required to log into PayPal for the initial payment.
Kinds of Embedded Payments
Embedded payments can include
- simple payments
- parallel payments
- chained payments
You can also enable preapprovals for future payments or enable shipping addresses
to be associated with embedded payments.
 Important:
Important: Payments
for digital goods must use the embedded payment flow. You cannot associate a preapproval
for future payments or enable shipping addresses in a payment for digital goods.
Embedded Payments Implementation Basics
To implement the embedded payment flow, you must
- include JavaScript code from PayPal on your checkout or payment web pages
- use the functions provided in the JavaScript to coordinate the PayPal flow with
the appearance of your web pages
- launch your preferred embedded payment flow, which is either the lightbox or minibrowser,
and redirect the sender's browser to the PayPal URL that supports embedded payments,
which is
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay?paykey=...
You must call the Pay API
operation to obtain a payment key before launching the embedded payment flow. If
the payment is specifically for digital goods, modify your Pay API
operation to specify that each receiver is receiving payment for digital goods.
Embedded Payment Experience
To the sender of a payment, the embedded payment experience appears to be built
into your website. The PayPal-supplied JavaScript provides all the code needed to
set up the flow as an IFRAME within the sender's browser and as a pop-up mini-browser
that appears in front of your website. Typically, the sender initiates a payment
by clicking a button:
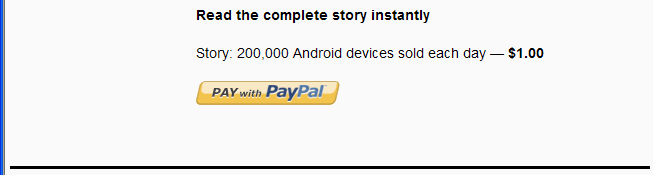
PayPal responds to the JavaScript that initiates the flow. If it is the first payment,
or if PayPal determines that the payment requires the sender to log in, PayPal displays
a Log In button in the IFRAME created by the JavaScript:

The IFRAME also allows the sender to sign up for a PayPal account or pay as a guest
without logging in.
Note: Guest checkout only provides the visual benefits of
an embedded payment. It does not reduce the payment steps.
After clicking Log In, PayPal displays a Log in to your PayPal account page
in the minibrowser. The sender enters an email address and password and can also
check a box, which allows the sender to skip this step for subsequent purchases:
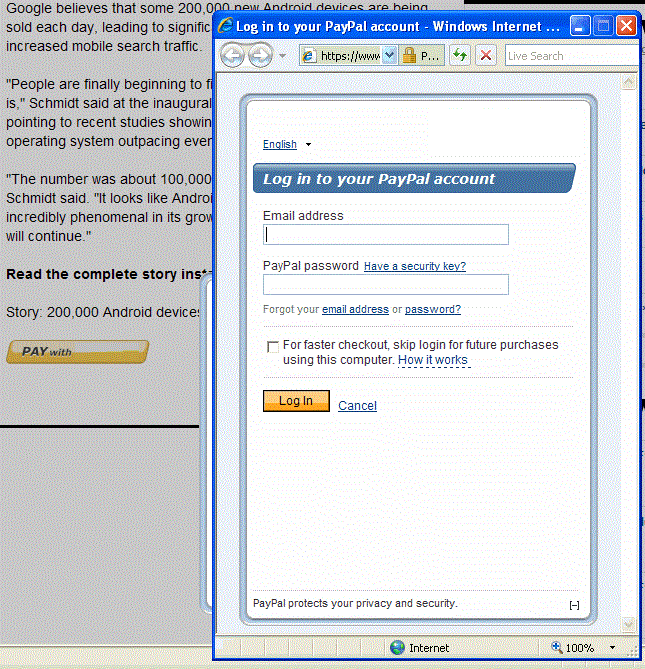
The checkbox controls the remember me behavior
for log in. This behavior allows the sender to skip the log in step in cases where
there is little risk of the account being misused.
 Important:
Important: Opting
in to the
remember me behavior
does not guarantee that the sender will not be asked to provide log in credentials.
After logging in, PayPal displays the You are about to pay page,
sometimes called the review your payment page
in the minibrowser:
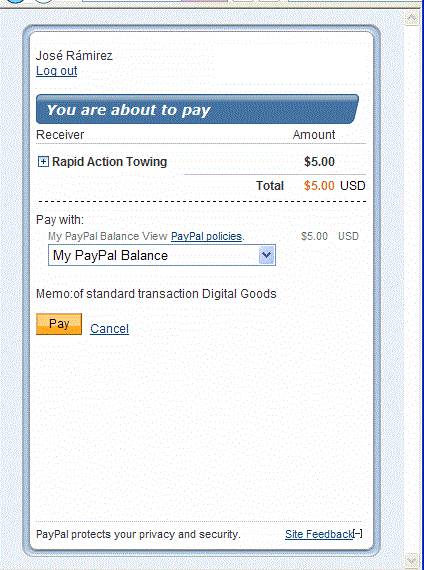
If the sender chooses Cancel, PayPal redirects the sender's browser
to the cancel URL specified in the Pay API operation's request message. If the sender
chooses Pay, the Thank you for using PayPal page
appears in the minibrowser:
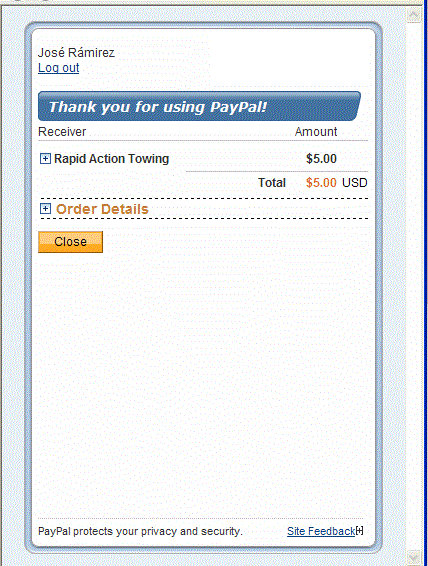
When the sender clicks Close, PayPal redirects the sender's browser
to the return URL specified in the Pay API operation's request message.
Note: You are responsible for closing the minibrowser after
PayPal redirects to the page specified in either the return or cancel URL. PayPal
provides a JavaScript function that you call to close a PayPal minibrowser or lightbox.
For subsequent payments in which PayPal does not require the account holder to log
in again and the account holder has chosen to be remembered, the PayPal payment
pages appear in a lightbox rather than in a minibrowser and PayPal bypasses the
log in steps. For these payments, the actions you take to launch the flow and close
the lightbox, remain the same. For example, the lightbox for reviewing a payment
would appear in your page as follows:
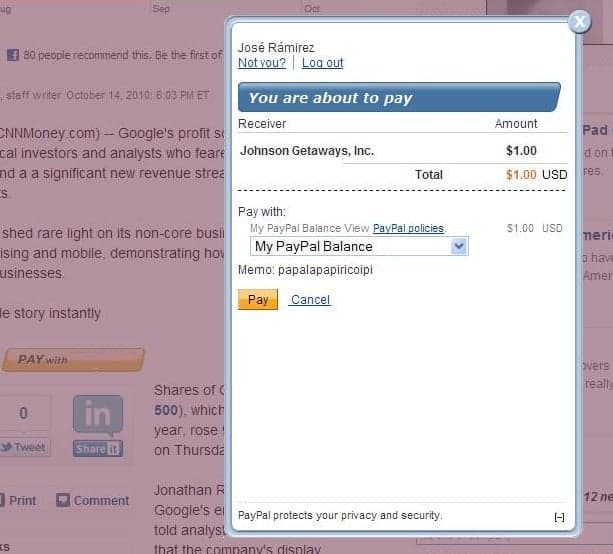
The lightbox containing the confirmation would appear in your page as follows:
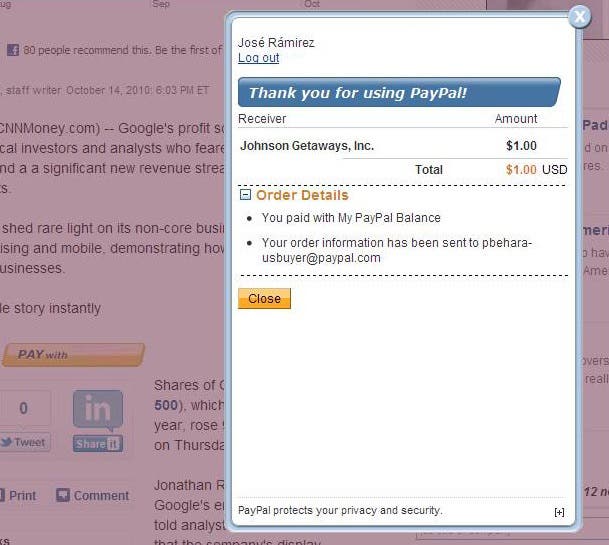
Preapprove Future Payments Checkbox
You can add a Preapprove future payments checkbox to the sender's
embedded payment experience, which enables the sender to preapprove subsequent payments.
If you specify both a payment key and a preapproval key when you call the Pay API
operation, PayPal displays the checkbox on the payment page in the minibrowser:

If the payment sender checks the preapproval box, the confirmation page provides
details about the preapproval:
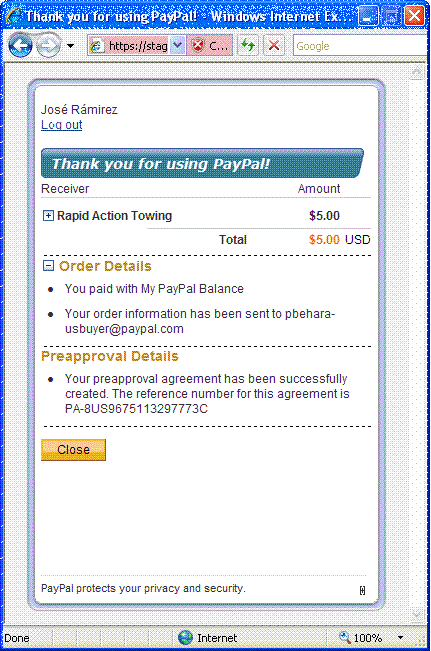
Note: Unless there is an error with the payment itself, PayPal
transfers the money regardless of whether the preapproval for future payments was
successful.
Shipping Address Information
You can display and collect shipping address information. PayPal displays the default
shipping address when you setsenderOptions.requireShippingAddressSelection to true in
your request to SetPaymentOptions:
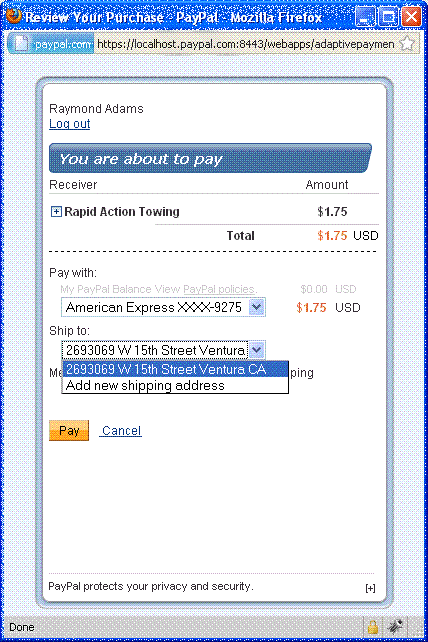
The sender of a payment can select one of the available shipping addresses or add
a new shipping address by selecting Add new shipping address from
the Ship to: drop-down menu:
Embedded Payment Experience
To the sender of a payment, the embedded payment experience appears to be built
into your website. The PayPal-supplied JavaScript provides all the code needed to
set up the flow as an IFRAME within the sender's browser and as a pop-up mini-browser
that appears in front of your website.
Typically, the sender initiates a payment by clicking a button:

PayPal responds to the JavaScript that initiates the flow. If it is the first payment,
or if PayPal determines that the payment requires the sender to log in, PayPal displays
a Log In button in the IFRAME created by the JavaScript:

The IFRAME also allows the sender to sign up for a PayPal account or pay as a guest
without logging in.
Note: Guest checkout only provides the visual benefits of
an embedded payment. It does not reduce the payment steps.
After clicking Log In, PayPal displays a Log in to your PayPal account page
in the minibrowser. The sender enters an email address and password and can also
check a box, which allows the sender to skip this step for subsequent purchases:

The checkbox controls the remember me behavior
for log in. This behavior allows the sender to skip the log in step in cases where
there is little risk of the account being misused.
 Important:
Important: Opting
in to the remember me behavior does not guarantee that the sender will not be asked
to provide log in credentials.
After logging in, PayPal displays the You are about to pay page,
sometimes called the review your payment page in the minibrowser:

If the sender chooses Cancel, PayPal redirects the sender's browser
to the cancel URL specified in the Pay API operation's request message. If the sender
chooses Pay, the Thank you for using PayPal page
appears in the minibrowser:

When the sender clicks Close, PayPal redirects the sender's browser
to the return URL specified in the Pay API operation's request message.
Note: You are responsible for closing the minibrowser after
PayPal redirects to the page specified in either the return or cancel URL. PayPal
provides a JavaScript function that you call to close a PayPal minibrowser or lightbox.
For subsequent payments in which PayPal does not require the account holder to log
in again and the account holder has chosen to be remembered, PayPal bypasses the
log in steps.
For example, the lightbox for reviewing a payment would appear in your page as follows:

The lightbox containing the confirmation would appear in your page as follows:

The actions you take to launch the flow and close the lightbox are the same steps
you take for the minibrowser.
Preapprove Future Payments Checkbox
You can add a Preapprove future payments checkbox to the sender's
embedded payment experience, which enables the sender to preapprove subsequent payments.
If you invoke the embedded payment flow, passing both a payment key obtained by
calling Pay and
a preapproval key obtained by callingPreapproval,
PayPal displays the checkbox on the payment page:

If the payment sender checks the preapproval box, the confirmation page provides
details about the preapproval:

Note: Unless there is an error with the payment itself, PayPal
transfers the money regardless of whether the preapproval for future payments was
successful.
Embedded Preapproval Experience
Adaptive Payments provides a preapproval experience using a mini-browser.You can
invoke the embedded preapproval flow by passing the preapproval key. Here is an
example :
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/preapproval?preapprovalKey
=PA-xxxxxxxxxxxx&expType=mini
PayPal first asks the user to log into their PayPal account:
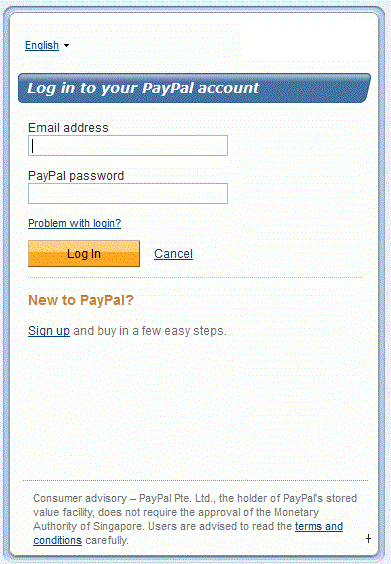
After signing in, the user is presented with a consent form that the user must agree
to:
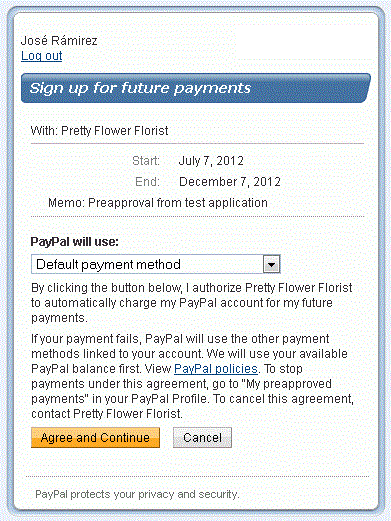
If the seller has enabled PIN code entry, after consenting to the agreement,
the
user is prompted to enter a PIN code by the seller:
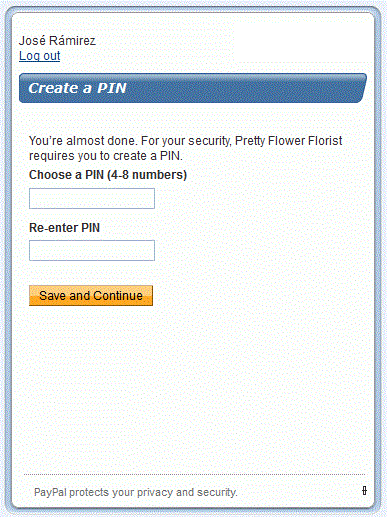
Finally, the user is presented with a confirmation screen:
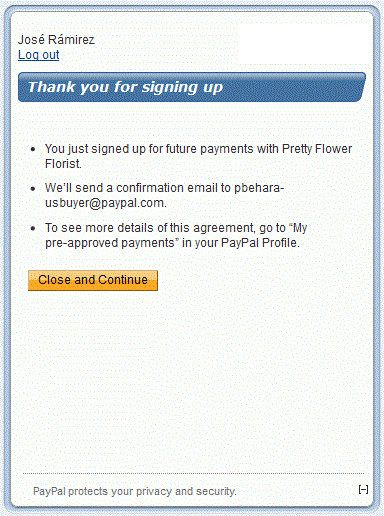
Shipping Address Selection
You can display and collect shipping address information for a transaction with
the embedded payment flow. PayPal displays the default shipping address when you
set senderOptions.requireShippingAddressSelection to true in
your request to SetPaymentOptions:

The sender of a payment can select one of the available shipping addresses or add
a new shipping address by selecting Add new shipping address from
the Ship to: drop-down menu:
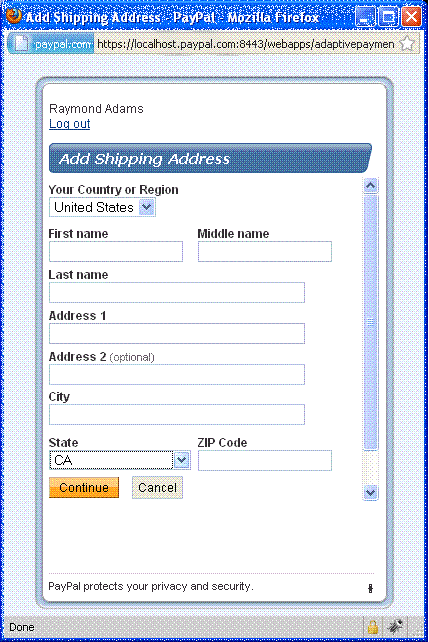
After the sender of the payment clicks Pay, PayPal displays the selected
shipping address on the Thank you for using PayPal page:
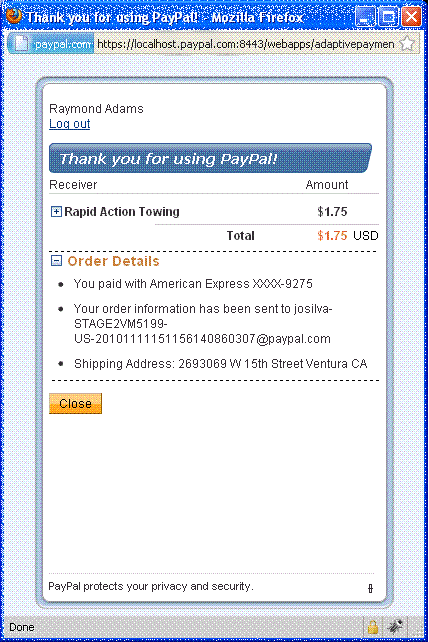
You can call the GetShippingAddresses API
operation to obtain the selected shipping address for the transaction using the
key assoicated with the payment.
Setting Up Web Pages to Invoke the Embedded Payment Flow Using a Lightbox
Use the JavaScript functions in https://www.paypalobjects.com/js/external/dg.js to
set up and control the embedded payment flow. This example shows how to initiate
the embedded payment flow after obtaining a payment key.
This example assumes that you obtain a payment key before initiating the flow and
that the key does not change or expire before the sender completes the flow.
To set up a web page to invoke the embedded payment flow:
- Call the
Pay API
operation to obtain a valid pay key.
- Create your form or button.
- You must include the pay key and redirect to
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay.
- Optionally, include a preapproval key if you want to enable the selection of Preapproval
for future payments
- Specify that a lightbox opens in the PayPal-created
IFRAME, PPDGFrame.
- Set the
expType parameter
to indicate your preference for the context in which the PayPal payment flow is
displayed. You must specify light for
lightbox.
<form action=
"https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay"
target="PPDGFrame">
<input id="type" type="hidden" name="expType" value="light">
<input id="paykey" type="hidden" name="paykey" value="
AP-..."> <input id="preapprovalkey" type="hidden" name="preapprovalkey" value="PA-..."> <input type="submit" id="submitBtn" value="Pay with PayPal"> </form>
Note: To modify an existing application to use the embedded
payment flow, change the redirect fromhttps://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_ap-payment&paykey=... to
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay?
paykey=... after obtaining the pay key.- Include the PayPal JavaScript functions from
dg.js.
<script src="https://www.paypalobjects.com/js/external/dg.js">
</script>
- Create an embedded flow object and associate it with your payment
form or button.
<script>
var dgFlow = new PAYPAL.apps.DGFlow({ trigger: 'submitBtn' });
</script>
On the pages you identify as the return and cancel URLs in the Pay API
operation, you must include the PayPal JavaScript functions from dg.js and
close the PayPal window, as in the following example:
dgFlow = top.dgFlow || top.opener.top.dgFlow;
dgFlow.closeFlow();
top.close();
Setting Up Web Pages to Invoke the Embedded Payment Flow Using a Minibrowser
Use the JavaScript functions in https://www.paypalobjects.com/js/external/apdg.js to
set up and control the embedded payment flow. This example shows how to initiate
the embedded payment flow after obtaining a payment key.
This example assumes that you obtain a payment key before initiating the flow and
that the key does not change or expire before the sender completes the flow.
To set up a web page to invoke the embedded payment flow:
- Call the
Pay API
operation to obtain a valid pay key.
- Create your form or button.
- You must include the pay key and redirect to
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay.
- Optionally, include a preapproval key if you want to enable the selection of Preapproval
for future payments
- Set the
expType parameter
to mini to
indicate your preference for the context in which the PayPal payment flow is displayed.
<form action=
"https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay"
target="PPDGFrame">
<input id="type" type="hidden" name="expType" value="mini">
<input id="paykey" type="hidden" name="paykey" value="
AP-..."> <input id="preapprovalkey" type="hidden" name="preapprovalkey" value="PA-..."> <input type="submit" id="submitBtn" value="Pay with PayPal"> </form>
Note: To modify an existing application to use the embedded
payment flow, change the redirect fromhttps://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_ap-payment&paykey=... to
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay?
paykey=... after obtaining the pay key.- Include the PayPal JavaScript functions from
apdg.js.
<script src="https://www.paypalobjects.com/js/external/apdg.js">
</script>
- Create an embedded flow object and associate it with your payment
form or button.
<script>
function <<returnFunctionName>>() {
<<Your code goes here.>>
}
</script>
The following minibrowser return script can be used to determine whether the payment
successfully completed:
PAYMENTDETAILS=$(wget --output-document=- \
--quiet \
--header="X-PAYPAL-SERVICE-VERSION: 1.0.0" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-USERID: $APIUSER" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-PASSWORD: $APIPASS" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-SECURITY-SIGNATURE: $APISIG" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-REQUEST-DATA-FORMAT: NV" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-RESPONSE-DATA-FORMAT: NV" \
--header="X-PAYPAL-APPLICATION-ID: $APPLICATIONID" \
--post-data="payKey=$PAYKEY&requestEnvelope.errorLanguage=en_US" \
https://www.paypal.com/AdaptivePayments/PaymentDetails)
if echo $PAYMENTDETAILS | grep -q "\&status=COMPLETED"
then echo "Thank you for approving pay key $PAYKEY"
else echo "Sorry, you were unable to approve pay key $PAYKEY. Please try another transaction!"
fi
Displaying and Collecting Shipping Addresses
PayPal displays the default shipping address and allows the payment sender to change
the address when you setsenderOptions.requireShippingAddressSelection to true in
your request to the SetPaymentOptions API
operation. You call theGetShippingAddresses API
operation to obtain the selected shipping address after invoking the embedded payment
flow.
The steps in this example assume that you have implemented the JavaScript for invoking
the embedded payment flow, that you have set up your button or form to invoke the
flow, and that you have included the code to close the window associated with the
flow.
To display and collect the selected shipping address
- Call the
Pay API
operation with actionType set
to CREATE to
obtain a payment key.
- Set
senderOptions.requireShippingAddressSelection to true in
your request to SetPaymentOptions and
call the API operation.
- Redirect the payment sender's browser to the embedded payment flow at
https://www.paypal.com/webapps/adaptivepayment/flow/pay?paykey=...after
obtaining the pay key.
- After returning from the flow, call the
GetShippingAddresses API
operation to obtain the selected shipping address.
Guest Payments
Adaptive payments supports guest payments, which are payments using
a sender's credit card without logging into PayPal to complete the transaction.The
sender is not explicitly identified as a PayPal account holder during the transaction
and is not required to have a PayPal account.
Each receiver of a guest payment must be a verified PayPal Business Verified or
Premier Verified account holder.
PayPal handles guest payments in the same way that it handles explicitly approved
payments. Instead of logging into PayPal to complete transaction, the sender provides
credit card information on the PayPal payment screen:
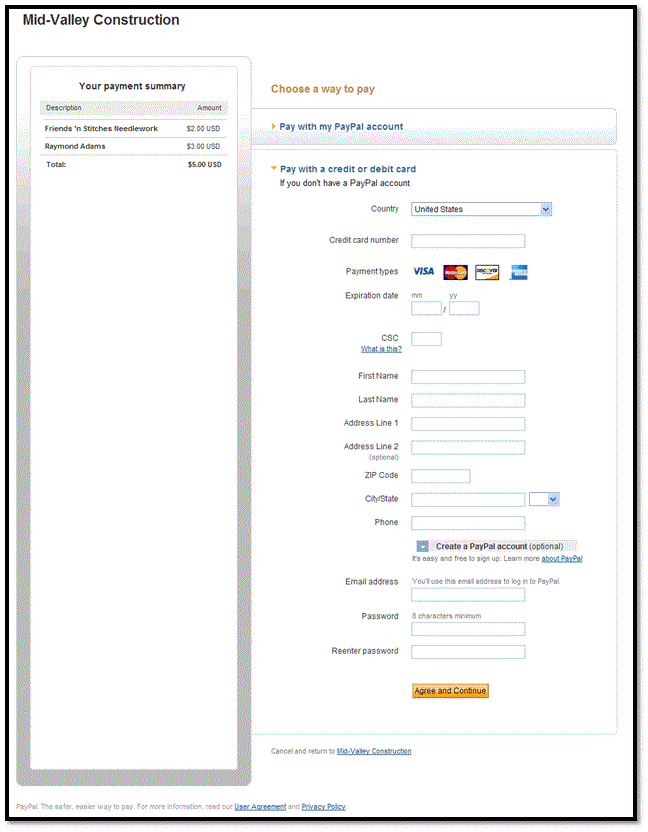
Note: For European Union countries, only 10 guest payments
are allowed per card.
Fee Payment Configuration
You can set up a payment transaction so that either the sender of a payment pays
the fee or the receivers of a payment pay the fee. If receivers pay the fee, you
can specify whether the primary receiver in a chained payment pays the entire fee
or whether all receivers pay a portion of the fee.
You can specify who pays these fees. Fee payment configurations include:
Note: Fees are determined by PayPal and are based on criteria,
such as the transaction volume of the receiver. In the examples that follow, the
fees shown are representative only and not actual fees.
Sender Pays the Fee
The sender can pay a fee for a simple payment, parallel payment, or a chained payment.
The following example shows fees being paid by the sender of a parallel payment,
based on the assessment for each receiver:
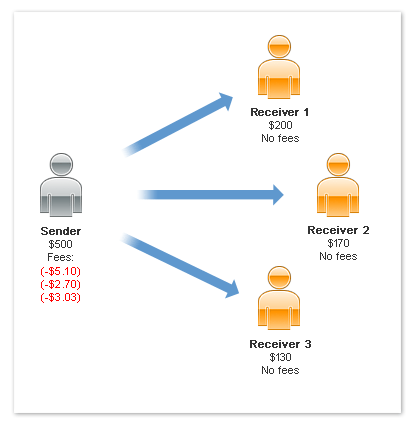
In this example, the sender pays a total of $510.83, which includes all fees.
Note: The scenario above is an example only and is not representative
of actual PayPal fees.
Receiver Pays the Fee in a Parallel Payment
If the receivers pay the fee in a parallel payment, each receiver pays a portion
of the fee, based on their assessment. The following example shows the receivers
paying the fees:

Note: The scenario above is an example only and is not representative
of actual PayPal fees.
Each Receiver Pays the Fee in a Chained Payment
If the receivers pay the fee in a chained payment, each receiver pays a portion
of the fee, based on their assessment. The following example shows the receivers
paying the fees:
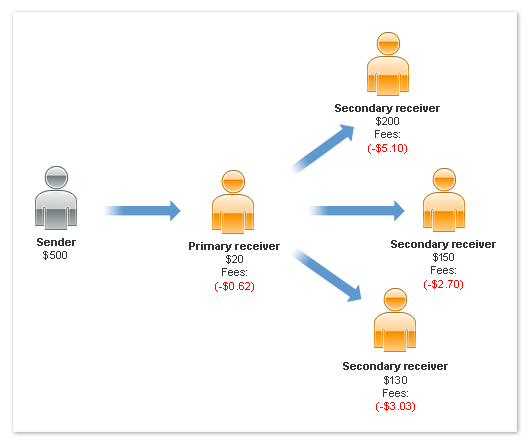
In this example, the primary receiver, identified as the merchant, pays a fee for
$20 received. Each of the other receivers also pay a fee on the amount each receives.
Note: The scenario above is an example only and is not representative
of actual PayPal fees.
Primary Receiver Pays the Fee in a Chained Payment
If only the primary receiver pays the fee in a chained payment, other receivers
pay no fees. The fees paid by the primary receiver, however, are based upon the
total fees assigned to all receivers. The following example shows only the primary
receiver, identified as the merchant, paying all fees:
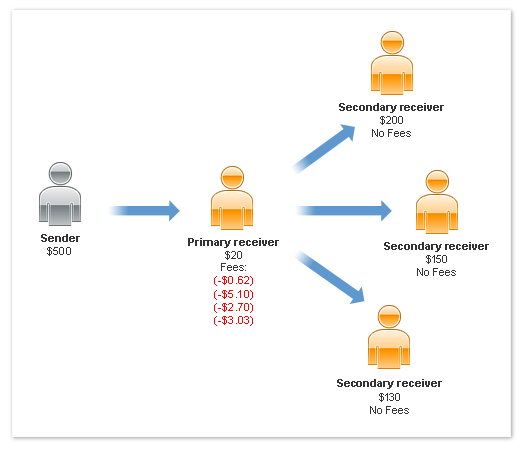
Note: The scenario above is an example only and is not representative
of actual PayPal fees.
Click here to view normal PayPal integration
Click here to view normal PayPal Pro integration







 b. Now your web page will have the chart control :
b. Now your web page will have the chart control :






































